AddPolygonToRegion(RasterRegionXForm,IList<LeadPoint>,LeadFillMode,RasterRegionCombineMode) Method
public void AddPolygonToRegion(RasterRegionXForm xform,IList<LeadPoint> points,LeadFillMode fillMode,RasterRegionCombineMode combineMode)
public void addPolygonToRegion(RasterRegionXForm xform,List<LeadPoint> points,Path.FillType fillType,RasterRegionCombineMode combineMode)
public:void AddPolygonToRegion(RasterRegionXForm^ xform,IList<LeadPoint>^ points,LeadFillMode fillMode,RasterRegionCombineMode combineMode)
def AddPolygonToRegion(self,xform,points,fillMode,combineMode):
Parameters
xform
RasterRegionXForm object that LEADTOOLS uses to translate between display coordinates and image coordinates. If you specify null in this parameter, the scalar fields default to 1, the offsets default to 0, and the view perspective defaults to the image view perspective.
points
A collection of LeadPoint objects. The points in the collection must be in the order in which the vertices of the polygon are connected. To create the line that closes the polygon, the last point in the collection is connected to the first point of the collection.
fillMode
Indicates how to handle complex crossing lines.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| LeadPoint.Winding | All pixels that are inside the resulting exterior lines are in the region. |
| LeadFillMode.Alternate | The region includes the area between odd-numbered and even-numbered polygon sides on each scan line. |
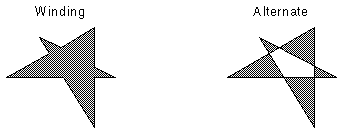
combineMode
The action to take regarding the existing image region, if one is defined.
To update an existing region, you specify how the new region is to be combined with the existing one using the combineMode parameter. For more information, refer to RasterRegionCombineMode.
For more information, refer to Creating a Region.
For more information, refer to Saving A Region.
For more information, refer to Working with the Existing Region.
This example will load an image, add a polygon region to it, and then run the InvertCommand to show the affected area before saving the image back to disk.
using Leadtools;using Leadtools.Codecs;using Leadtools.ImageProcessing;using Leadtools.ImageProcessing.Core;using Leadtools.ImageProcessing.Color;using Leadtools.Dicom;using Leadtools.Drawing;using Leadtools.Controls;using Leadtools.Svg;public void AddPolygonToRegionExample(){RasterCodecs codecs = new RasterCodecs();string srcFileName = Path.Combine(LEAD_VARS.ImagesDir, "Image1.cmp");string destFileName = Path.Combine(LEAD_VARS.ImagesDir, "Image1_AddPolygonToRegion.bmp");// Load the imageRasterImage image = codecs.Load(srcFileName);// Add a polygon regionRasterRegionXForm xform = new RasterRegionXForm();xform.ViewPerspective = RasterViewPerspective.TopLeft;xform.XOffset = 0;xform.YOffset = 0;xform.XScalarDenominator = 1;xform.XScalarNumerator = 1;xform.YScalarDenominator = 1;xform.YScalarNumerator = 1;int x1 = image.ImageWidth / 4;int y1 = image.ImageHeight / 4;int x2 = image.ImageWidth / 3;int y2 = image.ImageHeight / 3;LeadPoint[] pts ={new LeadPoint(x1, y1),new LeadPoint(x2, y1),new LeadPoint(x1, y2),new LeadPoint(x2, y2)};image.AddPolygonToRegion(xform, pts, LeadFillMode.Winding, RasterRegionCombineMode.Set);// Draw something on the imageInvertCommand command = new InvertCommand();command.Run(image);// Save the imagecodecs.Save(image, destFileName, RasterImageFormat.Bmp, 24);image.Dispose();codecs.Dispose();}static class LEAD_VARS{public const string ImagesDir = @"C:\LEADTOOLS23\Resources\Images";}
import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.junit.*;import org.junit.runner.JUnitCore;import org.junit.runner.Result;import org.junit.runner.notification.Failure;import static org.junit.Assert.*;import leadtools.*;import leadtools.codecs.*;import leadtools.imageprocessing.core.*;import leadtools.svg.*;import leadtools.imageprocessing.CloneCommand;import leadtools.imageprocessing.FillCommand;import leadtools.imageprocessing.FlipCommand;import leadtools.imageprocessing.GrayscaleCommand;import leadtools.imageprocessing.color.InvertCommand;import leadtools.imageprocessing.color.PosterizeCommand;public void addPolygonToRegionExample() {final String LEAD_VARS_IMAGES_DIR = "C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Resources\\Images";RasterCodecs codecs = new RasterCodecs();String srcFileName = combine(LEAD_VARS_IMAGES_DIR, "Image1.cmp");String destFileName = combine(LEAD_VARS_IMAGES_DIR, "Image1_AddPolygonToRegion.bmp");// Load the imageRasterImage image = codecs.load(srcFileName);// Add a polygon regionRasterRegionXForm xform = new RasterRegionXForm();xform.setRasterViewPerspective(RasterViewPerspective.TOP_LEFT);xform.setXOffset(0);xform.setYOffset(0);xform.setXScalarDenominator(1);xform.setXScalarNumerator(1);xform.setYScalarDenominator(1);xform.setYScalarNumerator(1);int x1 = image.getImageWidth() / 4;int y1 = image.getImageHeight() / 4;int x2 = image.getImageWidth() / 3;int y2 = image.getImageHeight() / 3;LeadPoint[] pts = { new LeadPoint(x1, y1), new LeadPoint(x2, y1), new LeadPoint(x1, y2), new LeadPoint(x2, y2) };image.addPolygonToRegion(xform, pts, LeadFillMode.WINDING, RasterRegionCombineMode.SET);// Draw something on the imageInvertCommand command = new InvertCommand();command.run(image);// Save itcodecs.save(image, destFileName, RasterImageFormat.BMP, 24);// Clean upimage.dispose();codecs.dispose();assertTrue("file unsuccessfully saved to " + destFileName, (new File(destFileName)).exists());System.out.printf("File saved successfully to %s%n", destFileName);}
© 1991-2024 LEAD Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
